➤Summary
The phishing campaign India landscape has evolved rapidly in 2025, with new sophisticated attacks targeting organizations, government agencies, and enterprises across the country. One of the most alarming cases involves an Income Tax Department phishing attack, where cybercriminals impersonated official tax authorities to distribute AsyncRAT malware through deceptive emails 😨. This growing trend reflects a larger shift in how attackers use social engineer techniques, malware chains, and digital impersonation to bypass trust and security. In this in-depth analysis, we explore how the attack unfolds, why it matters, how it connects with broader threats like the APT36 DeskRAT operation, and what security practitioners can do to counter these threats effectively.
The Rising Complexity of Tax-Themed Cyberattacks
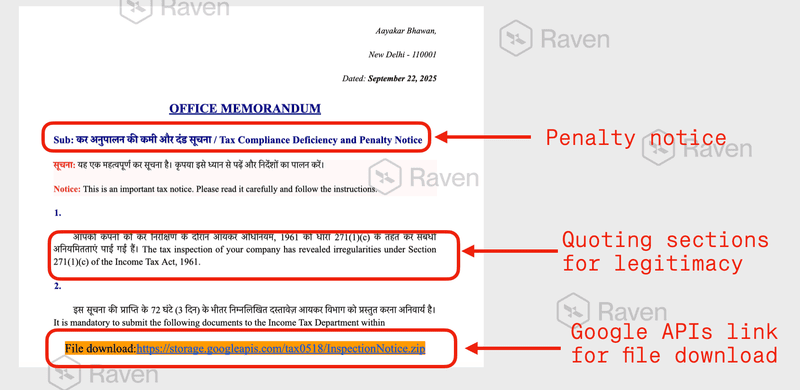
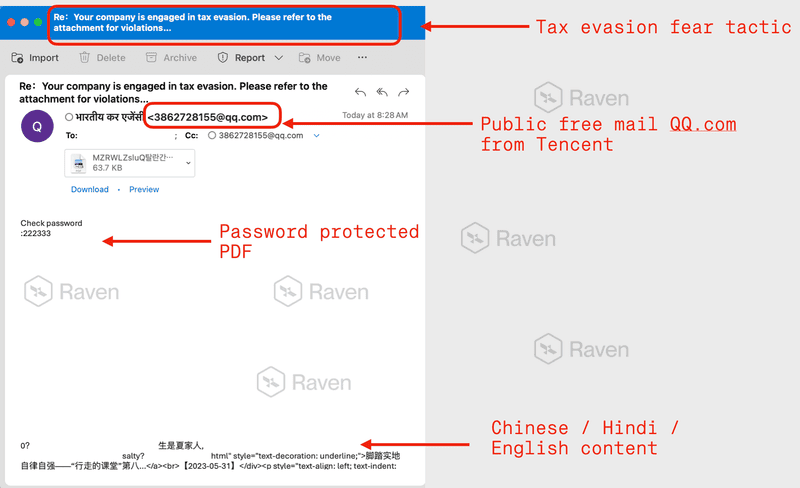
The recent attack began with emails crafted to resemble official notices from India’s Income Tax Department. These phishing email messages referenced tax laws, compliance deadlines, and legal consequences, applying psychological pressure to create urgency 📌. They were written in both English and Hindi, included accurate branding, and passed SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication—making them appear completely legitimate even to experienced professionals. Attackers distributed password-protected ZIP files or cloud-hosted documents inside these messages, a tactic specifically designed to bypass traditional scanning tools. This is a clear example of how modern cybercrime blends deception with stealth to create high-success-rate attacks.
Inside the Income Tax Department Phishing Attack
This section details how the Income Tax Department phishing attack deployed its payload. Once the recipient opened the ZIP file, a disguised executable triggered a shellcode-based loader that launched AsyncRAT malware silently. The RAT connected to external command-and-control servers, enabling attackers to steal data, monitor systems, execute commands, and move laterally within the network. Attackers even disguised one variant as a “GoTo Resolve updater,” exploiting trust in legitimate remote support tools. The attack is a reminder that no file format is safe when social engineer methods are used cleverly 🛑.
Malicious Emails Deliver AsyncRAT
The phishing campaign escalated further through two highly engineered malware delivery mechanisms. The first phishing variant posed as a Tax Compliance Deficiency and Penalty Notice, directing victims to download a password-protected ZIP file or follow a Google Docs URL embedded in the fake Income Tax Department memo. Once extracted, the archive revealed a 10.48 MB shellcode loader classified as Trojan.Shellcode and Fragtor.
This multi-stage payload was designed for stealth and resilience. It executed through regsvr32 proxy loading, a fileless execution technique that abuses trusted Windows utilities to avoid static signature-based antivirus detection. Because regsvr32 is a legitimate system binary, the malicious loader could bypass multiple EDR engines without triggering alerts.
Network telemetry linked this stage to AsyncRAT and ResolverRAT command-and-control servers, with JA3 SSL fingerprints matching well-known remote administration tool families. This strongly indicates that the attackers were using established RAT infrastructure to manage post-exploitation activity, exfiltrate data, and maintain persistent access.
The redirect URLs embedded inside the phishing email’s Google APIs link led directly to the download of multiple malicious shellcode loaders used in the operation.
A second, more sophisticated attack variant deployed a 23.34 MB executable named GoToResolveUnattendedUpdater.exe, which was identified as a rogue remote-access backdoor classified as Hacktool.LogMeIn. Masquerading as an update package for GoToResolve—an authentic remote IT management platform—the malware attempted to blend into enterprise environments where such tools are common.
Upon execution, the binary loaded a suspicious DLL named RstrtMgr.dll, a library historically abused by ransomware families including Conti and Cactus to terminate security processes, escalate privileges, and establish persistence.
The malicious updater exhibited full remote administration capabilities, including live screen sharing, file transfer, and remote command execution. These features indicate that attackers planned interactive intrusion operations, most likely for lateral movement, internal reconnaissance, and high-value data extraction once initial compromise had been achieved.
Connection to the APT36 DeskRAT Malware Operation
This phishing campaign is not an isolated incident. A correlated investigation published by Darknet Search (https://darknetsearch.com/) revealed that APT36, a known threat actor targeting Indian defense and Goveernment entities, deployed a Golang-based DeskRAT malware capable of infecting both Linux (including BOSS Linux) and Windows systems.
The similarities are striking:
- Both attacks use phishing as the initial access vector.
- Both disguise malicious files inside archives.
- Both deploy remote access trojans for espionage and long-term infiltration.
You can read the related APT36 analysis for context here:
🔗 https://darknetsearch.com/knowledge/news/en/apt36-malware-campaign-revealed-golang-based-deskrat-attack-on-indian-government-2025-report/
Together, they form a pattern demonstrating how threat groups exploit institutional trust and digital transformation to infiltrate networks stealthily.
Why Attackers Focus on Government-Themed Phishing
Cybercriminals intentionally select government-themed lures because they trigger urgency, fear, and compliance. A notice from a tax authority is much more effective than a random phishing email. Attackers exploit:
- Trust in authority
- Familiar legal terminology
- The stress of potential penalties
This psychological manipulation is textbook social engineer methodology 🤯. When combined with modern malware frameworks, the success rate becomes extremely high.
Case Study Dark Web Monitoring Findings
Using a case study dark web monitoring approach, analysts discovered early indicators of the AsyncRAT infrastructure. Several C2 domains and IPs linked to the campaign were circulating on dark web forums before the public reporting. This highlights the importance of early intelligence gathering for preventing breaches. Monitoring the dark web for leaked credentials, attack chatter, or malware configuration files allows organizations to act before damage occurs. Cyber defenders must adopt proactive intelligence, not just reactive defense.
Critical Risks Organizations Must Understand
A modern phishing campaign India attack can lead to severe consequences, including:
- Unauthorized remote access
- Credential theft
- Financial fraud
- Ransomware deployment
- Asset manipulation
- Intellectual property theft
- Targeted espionage
The risk is significantly higher for sectors like finance, infrastructure, telecom, and Goveernment agencies. Even a single click can compromise entire networks 💥.
Checklist: How to Detect Tax-Themed Phishing Emails
To help readers stay protected, here is a quick detection checklist (ideal for Google featured snippets):
Checklist for Identifying Tax-Themed Phishing Emails:
- Look for urgent deadline-based language.
- Check if the email demands downloading ZIP files.
- Verify sender domain authenticity manually.
- Inspect for spelling or formatting anomalies.
- Hover over links before clicking.
- Avoid opening unidentified attachments.
- Contact the official agency directly for confirmation.
Practical Tip for Defenders
Enable attachment sandboxing and behavioral analysis in your email security system. Password-protected ZIP files are a common bypass method, and behavioral sandboxes can detect malicious loaders before they deploy AsyncRAT malware. 🛡️
Table: Comparison of AsyncRAT vs DeskRAT
| Feature | AsyncRAT | DeskRAT (APT36) |
| Language | .NET | Golang |
| Platforms | Windows | Windows & Linux |
| Purpose | Surveillance & remote access | Espionage & persistence |
| Delivery | Phishing ZIP files | Spear-phishing decoys |
| Stealth Level | Moderate | High |
What Should Security Practitioners Do Now?
For security practitioners, these attacks demonstrate that traditional defenses no longer suffice. Password-protected attachments, authentic-looking emails, and file-less loaders allow malware to bypass many standard tools.
Teams should implement:
- Zero-trust email filtering
- Endpoint behavior monitoring
- Network anomaly detection
- Dark web intelligence integration
- Employee awareness programs
- Strict attachment handling policies
An expert from the cybersecurity industry summarized it well:
“When phishing evolves faster than defenses, proactive intelligence becomes the real shield.”
Question & Answer
Q: Can organizations fully prevent modern phishing attacks?
A: Not fully—but they can dramatically reduce risk through layered security, user training, dark web monitoring, and real-time behavioral detection technologies.
Why This Phishing Campaign India Case Matters
This phishing campaign India incident represents more than just another malware delivery attempt. It exposes a systemic vulnerability: trust in digital government communication channels. As India accelerates e-filing, e-taxation, and online compliance systems, attackers will continue to weaponize this trust. The long-term solution requires coordinated effort between enterprises, government, and cybersecurity institutions 🧩.
Final Recommendations
- Validate any message claiming to be from a government authority.
- Never download ZIP files from unsolicited emails.
- Use multi-layered protection instead of relying on traditional antivirus.
- Integrate dark web monitoring to stay ahead of malware campaigns.
- Train teams regularly on spotting social engineer attacks.
For additional threat insights and related reports, visit:
🔗 https://darknetsearch.com/
Conclusion
The ongoing evolution of phishing campaign India threats—especially those involving AsyncRAT malware and advanced APT actors like APT36—highlights the urgent need for stronger cybersecurity frameworks. Organizations must invest in intelligence, training, proactive monitoring, and multi-layered protection strategies to confront these increasingly complex attacks 🚀.
To stay ahead of emerging threats and strengthen your organization’s security posture, take action now.
Discover much more in our complete guide
Request a demo NOW
Your data might already be exposed. Most companies find out too late. Let ’s change that. Trusted by 100+ security teams.
🚀Ask for a demo NOW →Q: What is dark web monitoring?
A: Dark web monitoring is the process of tracking your organization’s data on hidden networks to detect leaked or stolen information such as passwords, credentials, or sensitive files shared by cybercriminals.
Q: How does dark web monitoring work?
A: Dark web monitoring works by scanning hidden sites and forums in real time to detect mentions of your data, credentials, or company information before cybercriminals can exploit them.
Q: Why use dark web monitoring?
A: Because it alerts you early when your data appears on the dark web, helping prevent breaches, fraud, and reputational damage before they escalate.
Q: Who needs dark web monitoring services?
A: MSSP and any organization that handles sensitive data, valuable assets, or customer information from small businesses to large enterprises benefits from dark web monitoring.
Q: What does it mean if your information is on the dark web?
A: It means your personal or company data has been exposed or stolen and could be used for fraud, identity theft, or unauthorized access immediate action is needed to protect yourself.
Q: What types of data breach information can dark web monitoring detect?
A: Dark web monitoring can detect data breach information such as leaked credentials, email addresses, passwords, database dumps, API keys, source code, financial data, and other sensitive information exposed on underground forums, marketplaces, and paste sites.

